The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) isn’t just a legal obligation—it’s the key to safeguarding your business and securing long-term success when operating in the state.
Under the CCPA and its expansion and amendment in the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), consumers have more control over their personal information and how it’s handled by businesses. Failing to adhere to these regulations can result in hefty fines and penalties.
To achieve or maintain compliance, businesses need a thorough understanding of the regulation and keen attention to detail.
To help you ensure that your website is CCPA and CPRA-compliant, we’ve compiled a CCPA compliance checklist.
Who needs to comply with the CCPA?
The CCPA applies to all for-profit organizations that do business in California, and that meet any of the following criteria:
- They receive, process, or transfer data from 100,000 or more consumers or households in California every year.
- Their annual gross revenue from the preceding calendar year exceeds USD 26,625,000.
- At least 50 percent of their annual revenue comes from selling or sharing California residents’ personal data.
If any of these criteria apply to your business, failure to comply with the CCPA can lead to fines of up to US 7,988 per willful violation.
Check out our CCPA compliance checklist below to align your business with CCPA/CPRA privacy laws.
How does the CCPA define personal data?
With the latest information from the Officer of Attorney General website, the CCPA categorizes personal data into two pillars:
Personal information: This includes data that identifies, relates to, describes or can be associated with an individual or their household. Examples include:
- name
- Social Security number
- email address
- records of products purchased
- internet browsing history
- geolocation data
- fingerprints
- any other information reflecting an individual’s preferences and characteristics
Sensitive personal information: This is data that, if stolen or misused, can seriously harm an individual. Examples include:
- account log-in details
- financial accounts
- debit or credit card numbers and security codes
- passwords and credentials allowing access to an account
- precise geolocation
- content of private mail, email, and text messages
- biometric information that can identify a consumer
- a consumer’s health information
- information about racial or ethnic origin, religious or philosophical beliefs, or union membership
CCPA and CPRA compliance checklist
What do you need to do to ensure you’re compliant with both the CCPA and CPRA? Follow our checklist to kickstart the process.
1. Develop a comprehensive data privacy policy
A privacy policy details how your company collects, uses, shares and safeguards the personal information of customers or prospects who interact with your website. It informs customers of their data privacy rights and enables you to build trust by demonstrating your adherence to data privacy laws.
The CCPA requires you to be transparent about the type of data you collect from customers. As such, a CCPA-compliant privacy policy must include the following:
- type of information being collected and processed
- purpose(s) for collecting and processing this information
- how you’re collecting and processing this information, e.g. trackers in the browser
- how personal information is used, e.g. advertising, analytics
- how the information may be shared with third parties
- how individuals can request access to, change, move, or have their personal data deleted
- identity verification procedure for submitting a data subject access request
Since the CRPA amendments were introduced in 2023, your privacy policy should also include:
- a clause listing which personal data collected is categorized as sensitive, if applicable
- a statement advising that your customers have the right to have the information they have shared with you corrected or updated
- how individuals can opt out of their data being sold or shared; your website is required to have a clear “Do Not Sell Or Share My Personal Information” link
2. Disclose how your customers’ data is used
If you sell or share information about California consumers protected by the CCPA or CPRA, you must inform them before their data is sold or shared with third parties. You can achieve this using a consent management banner that appears when they visit your site.
The consent management banner should be easily noticeable and accessible on your website. Suitable locations or points in the user flow include:
- first point of contact, such as your landing pages and/or home page
- as part of a registration or signup process
- during the checkout process
- in the site’s header or footer
When informing users how their data is being used in a consent banner, follow these guidelines:
- Clearly explain what they are consenting to regarding the data collected, purposes for its use, who it may be shared with, etc.
- Provide the purposes for why you’re collecting their data, whether to improve the user experience, personalize content, target advertising, or other business interests.
- Specify the types of data being collected, which can include personal information (e.g. name, email, IP address) or for functions like browsing behavior via use of cookies or other tracking technologies.
- Provide equally accessible options for individuals to accept or decline the consent request, where relevant, or to opt out. Under the CCPA/CPRA, consumers can opt out of collection and processing of their sensitive personal information, e.g. with a link reading “Limit the Use of My Sensitive Personal Information” or comparable, or from sharing or sale of their personal information.
- Include a link to your privacy policy where they can find more detailed information.
3. Collect and store consent
The CCPA and CPRA do not require businesses to obtain consent from consumers before selling or sharing their personal information unless the information is that of minors. But they must enable people to opt out of the sale or sharing at any time.
Companies must also limit their use of sensitive personal information to what’s necessary to perform or provide goods or services reasonably expected by the average consumer requesting them.
Here are some best practices to collect and store consent data securely:
- Implement user-friendly mechanisms to collect consent, like a consent banner on your website.
- Collect consent directly from any visitor that’s over the age of 13 (including minors 13 to 16 years old), or from parents or legal guardians if they are under 13.
- Give users granular information and consent options to choose which types of data they’re willing to share, if they choose to.
- Ensure that visitors and customers can revisit their consent preferences and update or withdraw consent at any time.
- Be sure to understand the difference between personal information and “sensitive” personal information, what the consent requirements are for each, and how each must be handled.
To be compliant with the CCPA, websites must also honor the universal opt-out signal/mechanism, aka Global Privacy Control (GPC). This enables website visitors to set their privacy and consent preferences just once—using their browser—and then have those preferences applied on all sites they visit.
4. Securely maintain customer records
It’s as much a regulatory requirement to securely store consent information as it is to store personal data collected from users.
Additionally, consent records must be accessible for several purposes. For example, if users decide to change their preferences or opt out of sale or sharing, if users exercise their rights and make a data subject access request, or in case of an investigation or audit by the California Privacy Protection Agency.
A consent management platform (CMP) enables users’ consent information to be compliantly obtained or updated and securely stored, in addition to providing users with the information necessary for regulatory compliance, like the types of data collected and purposes of use.
5. Include a clear “Do Not Sell Or Share My Personal Information” link on your website homepage
A key requirement of the CCPA involves enabling website visitors to opt out of the sale of their data to, or sharing with, third-party vendors if they wish to.
In most cases, you won’t need to explicitly ask customers to opt-in before you can collect and sell their data, unless you’re knowingly collecting children’s data, but you will always need to provide an opt-out option.
That’s what a “Do Not Sell Or Share My Personal Information” link does, or a “Limit the Use of My Sensitive Personal Information” link for sensitive information. It directs individuals to a page where they can exercise their rights to opt out or access additional privacy information or controls.
Consider using a CMP to add this link and other required privacy information to the following parts of your website:
- the footer
- privacy policy
- consent banners
With Usercentrics CMP, you can fully customize its appearance to match your corporate branding or use a template. Design the colors, fonts, logos, links, buttons, and more.
Monitor the performance of the banner via the Analytics Dashboard and A/B Testing to see how customers interact with it and optimize the user experience.
6. Make sure that users can contact you
The CCPA/CPRA requires you to enable website visitors and customers to easily contact you regarding data requests or privacy concerns. Make this information easily accessible on your website. Doing so also helps build trust to allow you to collect personal (and potentially sensitive) information.
Businesses are also required to have a system to receive and respond to user requests, and retain request information for two years. For some businesses, the system will need to be automated if there is a lot of data involved and/or a large volume of user requests.
The CCPA/CPRA grants California users the right to:
- access the personal data you’ve collected about them and ask questions about it or make requests
- request changes or corrections to their data
- request a copy of their data and have it moved somewhere else (data portability)
- opt out of the sharing or sale of their data, or its use with automated decision-making technologies
- limit the use and disclosure of sensitive personal information
- have their data deleted
- experience no discrimination if they choose to opt out or otherwise exercise their rights
Companies are required to respond to reasonably verifiable user requests within 45 days, though that can be extended under certain circumstances for an additional 45 days.
7. Set up an identity verification system for users submitting requests
If a business cannot verify the consumer’s identity to an appropriate degree of certainty, it can deny the request. However, you must inform the consumer and explain why the request could not reasonably be verified or fulfilled.
Consumers need to be provided with reasonable means of verifying their identities, e.g. being able to attach documents to the contact form or other contact mechanism.
Make sure your website has a comprehensive and transparent privacy policy that informs users about all identity verification requirements and ways to submit, in addition to information on the collection of their personal data and their right to opt out of its sharing or sale.
8. Make data privacy an ongoing and company-wide operation
In addition to the necessary website functions and documentation to comply with the CCPA/CPRA, and the people responsible for implementing and managing them, data privacy should be something everyone in the company is involved with.
Employees in many departments, from IT to marketing to legal to sales to support need to access and use personal data collected from individuals, and should be trained to do so using security and privacy best practices.
Information about data privacy regulation requirements and how they specifically affect your business should be easily available, and it’s recommended to appoint a data privacy or protection officer to oversee privacy operations, enforce best practices, and oversee any issues, like in the case of a complaint or data breach.
Noncompliance with data privacy regulations like the GDPR and CCPA can result in data breaches and financial loss due to fines and other penalties. It also causes operational disturbances and loss of data, leading to downtime, loss of productivity and damage to your reputation and the trust of your customers and prospects, affecting revenue long-term.
Using a consent management platform to maintain compliance
A CMP helps you achieve and maintain CCPA compliance by collecting, storing, and managing your user consent data. With a high-performing CMP, you can:
- customize the design and layout of consent banners to match your website’s look and feel
- present users with clear and granular consent and opt-out options, including the freedom to revoke consent or adjust their privacy settings
- access integrations with third-party services, such as analytics platforms or advertising networks, to consolidate user consent data across tools and platforms
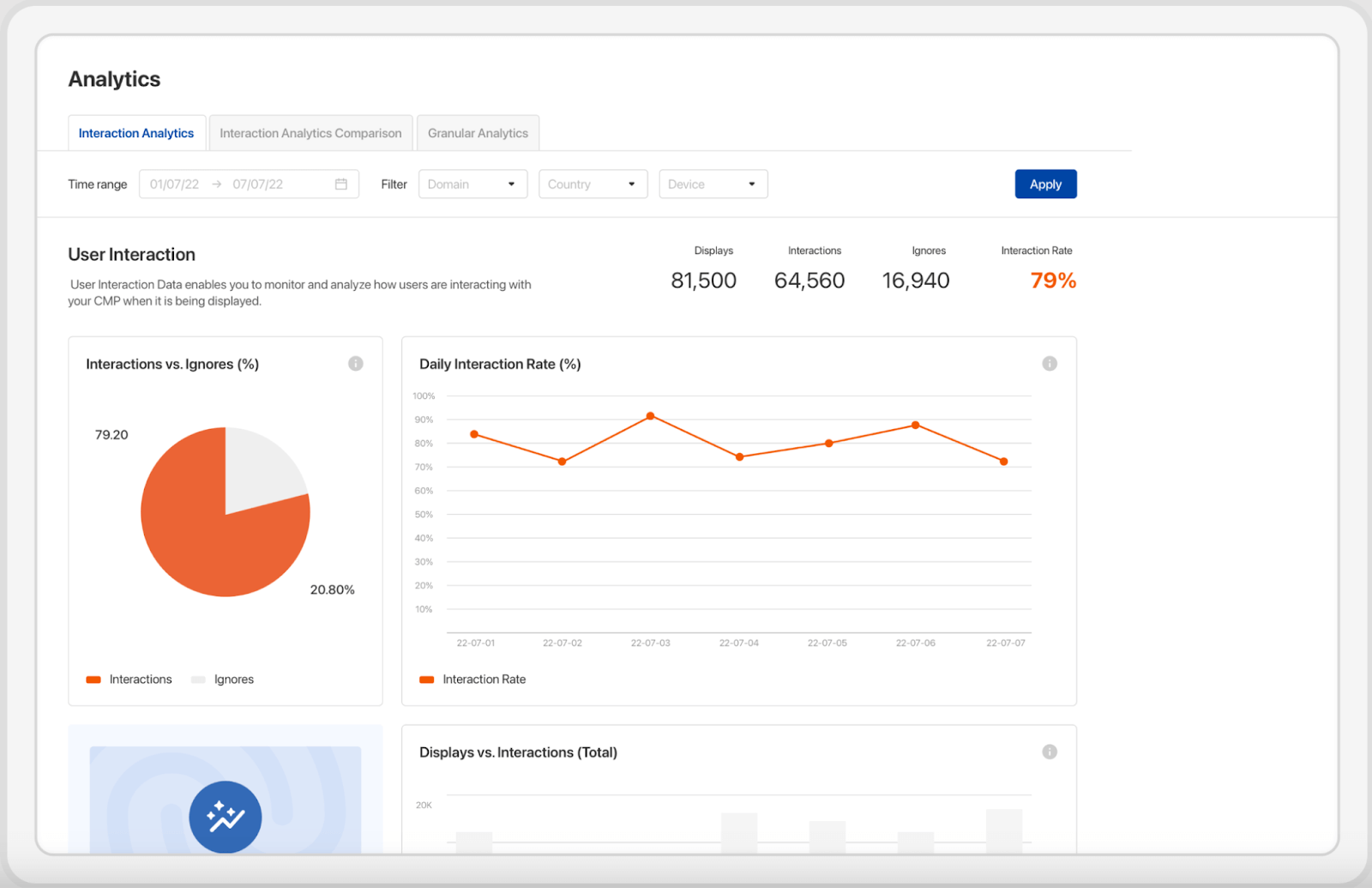
This analytics dashboard from the Usercentrics Consent Management Platform shows user interactions and consent decisions.
Maintain CCPA compliance with Usercentrics
Usercentrics Web CMP, Usercentrics App CMP, and Cookiebot™ Web CMP enable privacy compliance with the CCPA, CPRA and more, while also respecting the GPC signal.
Get in touch with one of our experts for answers to your CCPA and CPRA questions.
Usercentrics does not provide legal advice, and information is provided for educational purposes only. We always recommend engaging qualified legal counsel or privacy specialists regarding data privacy and protection issues and operations.




